PhD Chapter - Apa itu Unit Root
Posted by: admin 3 years, 2 months ago
(Comments)
Mengingat kembali apa itu pengertian dari Unit Root
note penting : tulisan ini merupakan catatan pribadi untuk kepentingan penulis, tidak ada tujuan mempublikasikannya ataupun menggunakannya untuk keperluan komersil, oleh karena itu penulis tidak bertanggung jawab atas kemiripan ataupun kesalahan dalam tulisan ini. Salam
Gini gan, untuk membuat pondasi yang kuat dalam pemahaman aye di Ekonometric, ane berniat bikin blog ini sebagai pengingat kalau aye lupa. Berikut adalah salah satu pemahaman sebelum kita masuk ke topik mengenai panel unit root dan akhirnya nanti melompat ke panel kointegrasi. Nah sebelum kita masuk ke sana kita harus paham dulu beberapa hal seperti.
Auto regresi
Unit root
dan cointegrasi
serta non stationer data
nah kali ini kita akan masuk terlebih dahulu ke pengertian mengenai unit root.
Tujuan ontologi ilmu akar unit :
Dalam statistik dan ekonometrik, uji akar unit digunakan untuk menguji adanya anggapan bahwa sebuah data time series tidak stasioner Gan.
Cara pengujian :
Uji yang biasa digunakan adalah uji augmented Dickey–Fuller.
Uji lain yang serupa yaitu Uji Phillips–Perron.
Hipotesis
Keduanya mengindikasikan keberadaan akar unit sebagai hipotesis null.
Asumsi
Perlu diketahui bahwa data yang dikatakan stasioner adalah data yang bersifat flat, tidak mengandung komponen trend, dengan keragaman yang konstan, serta tidak terdapat fluktuasi periodik.
Berikut adalah contoh pola data yang tidak stasioner:
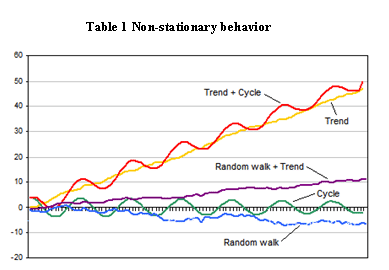
Kemudian kita usahakan menjadi stationer

Untuk diketahui adanya akar unit, maka dilakukan pengujian Dickey-Fuller (DF-test) sebagai berikut:
Jika variabel \( Y_t \)sebagai variabel dependen, maka akan diubah menjadi
.. (1) \(Y_t = \rho Y_{t-1} + U_t \)
Jika koefisien
[ Y_{t-1} , \rho= 1 ..(2)]
dalam arti hipotesis diterima, maka variabel mengandung unit root dan bersifat non-stasioner. Untuk mengubah trend yang bersifat non-stasioner menjadi stasioner dilakukan uji orde pertama (first difference)
[\bigtriangleup Y_{t} = (\rho-1) (Y_{t} – Y_{t-1} ]
Koefisien akan bernilai 0, dan hipotesis akan ditolak sehingga model menjadi stasioner.
Hipotesis yang digunakan pada pengujian augmented dickey fuller adalah:
H0 : ρ = 0 (Terdapat unit roots, variabel Y tidak stasioner)
H1 : ρ ≠ 0 (Tidak terdapat unit roots, variabel Y stasioner)
Kesimpulan hasil root test diperoleh dengan membandingkan nilai t-hitung dengan t-tabel pada tabel Dickey-Fuller.
Untuk pengujiannya dengan E-views agan bisa lihat di web menarik lain di sini gan
Kenapa sekolah PhD butuh waktu lama!?
Recent newsKali ini kita akan bahas kenapa sekolah PhD itu lama! Tanpa panjang lebar, berikut cara ngeles gw! Maksudnya berikut alasannya! Hope its relate with you!
read more4 days, 4 hours ago
Using Vertex AI for zero one and two three AI prediction
Recent newsHere is my documentation after learning the introduction of AI in courserERA.
read more3 weeks ago
Neural network with API for pre-trained API
Recent newsOverview
The Cloud Natural Language API lets you extract entities from text, perform sentiment and syntactic analysis, and classify text into categories.
read more3 weeks, 2 days ago
what is null result
Recent newsNull result in economic is when the output does not supporting your hypothesis
read more3 weeks, 4 days ago
3 weeks, 4 days ago
Fixing the issue in assumption of OLS step by step or one by one
Recent newsHi, I want to raise the issue related to know whether your OLS is ok or not.
read more1 month, 3 weeks ago
Meaning of 45 degree in economics chart
Recent newsThe **45-degree line** in economics and geometry refers to a line where the values on the x-axis and y-axis are equal at every point. It typically has a slope of 1, meaning that for every unit increase along the horizontal axis (x), there is an equal unit increase along the vertical axis (y). Here are a couple of contexts where the 45-degree line is significant:
read more2 months, 3 weeks ago

Collaboratively administrate empowered markets via plug-and-play networks. Dynamically procrastinate B2C users after installed base benefits. Dramatically visualize customer directed convergence without


Comments