Meaning of 45 degree in economics chart
Recent newsThe **45-degree line** in economics and geometry refers to a line where the values on the x-axis and y-axis are equal at every point. It typically has a slope of 1, meaning that for every unit increase along the horizontal axis (x), there is an equal unit increase along the vertical axis (y). Here are a couple of contexts where the 45-degree line is significant:
read more
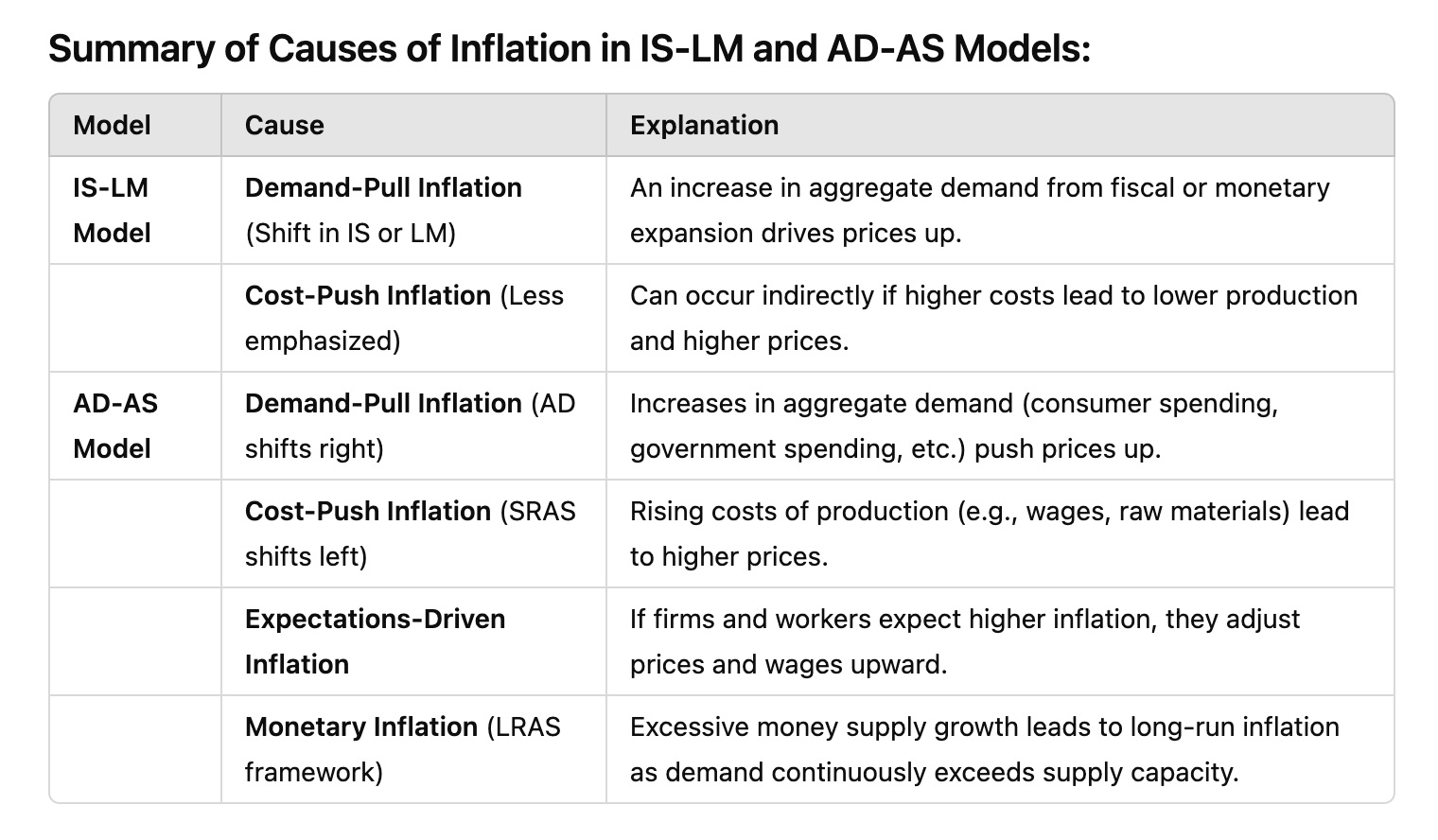



Comments