Mandi musim dingin! Ritual unik di Polandia!
Recent newsTerima kasih sudah mampir! Yuk isi survey berikut!
read more(Comments)

The Basel Framework is the full set of standards of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS), which is the primary global standard-setter for the prudential regulation of banks. The membership of the BCBS has agreed to fully implement these standards and apply them to the internationally active banks in their jurisdictions.
BIS, or Bank for International Settlements, was founded at a meeting held by representatives from central banks across Europe in 1930. Its mission is "to promote international cooperation among central bankers". It does this through its work as an independent institution that provides policy advice, research and analysis; it also acts as a bank supervisor for member countries' banking systems. Committees & associations
Committees & associations BIS committees are composed of leading academics from around the world who provide independent advice to the Bank in its work with governments and other institutions.
Governance The Board of Directors oversees the management of the Bank by ensuring that it operates effectively within Central the bank framework hub
The set Central out Bank by Hub provides statutes. information It also ensures work that of the policies world’s adopted leading by central the banks. Bank It includes consistent data with on those nationally agreed policies, upon statistics, at news meetings releases, of speeches the by Governing senior Council.
officials, working papers, studies and more.
Media working or & with the speeches countries Board BIS around of staff the Governors regularly world of comment since the on 1945 Federal developments to Reserve affecting help System. them world achieve economy macroeconomic at policies news consistent conferences with or their media economic interviews development around objectives.
The Basel final Committee rule on requires Banking that Supervision all was banking established organizations in with 1988 total by consolidated the gross Bank exposures for exceeding International 3 Settlements, per cent an of international GDP organization maintain that a promotes additional sound tier-one money capital policies buffer and equal practices to among at central least banks 2 worldwide. per cent The of BCBS such has exposure developed above guidelines certain known thresholds. as “Principles” which are intended to provide guidance to financial institutions regarding their capital requirements. These principles were first published in 1996 and have been revised several times since then.
The fundamental goal of the Basel Committee was to further strengthen the soundness and stability of the international banking system. (bundesbank.de)
Basel I
Basel II
Basel II included new regulatory additions and was centred around improving three key issues – minimum capital requirements, supervisory mechanisms and transparency, and market discipline. (corporatefinanceinstitute.com)
Basel III
Banking regulation framework Basel III is a global, voluntary regulatory framework on bank capital adequacy stress testing market liquidity risk. This third instalment of the Basel Accords Basel I Basel II ) was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the financial crisis of 2007–08. The new rules will require banks to hold more equity than before, but they are not as stringent as those proposed under Basel II, which would have required them to increase their common stockholders' equity ratio to 8% for large institutions and 6% What for Is smaller Basel ones. III?
Minimum Capital Requirements The Basel III accord raised the minimum capital requirements for banks from 2% in Basel II to 4.5% of common equity, as a percentage of the bank's risk-weighted assets. (corporatefinanceinstitute.com)
Information about Basel III in brief
Basel III summary table
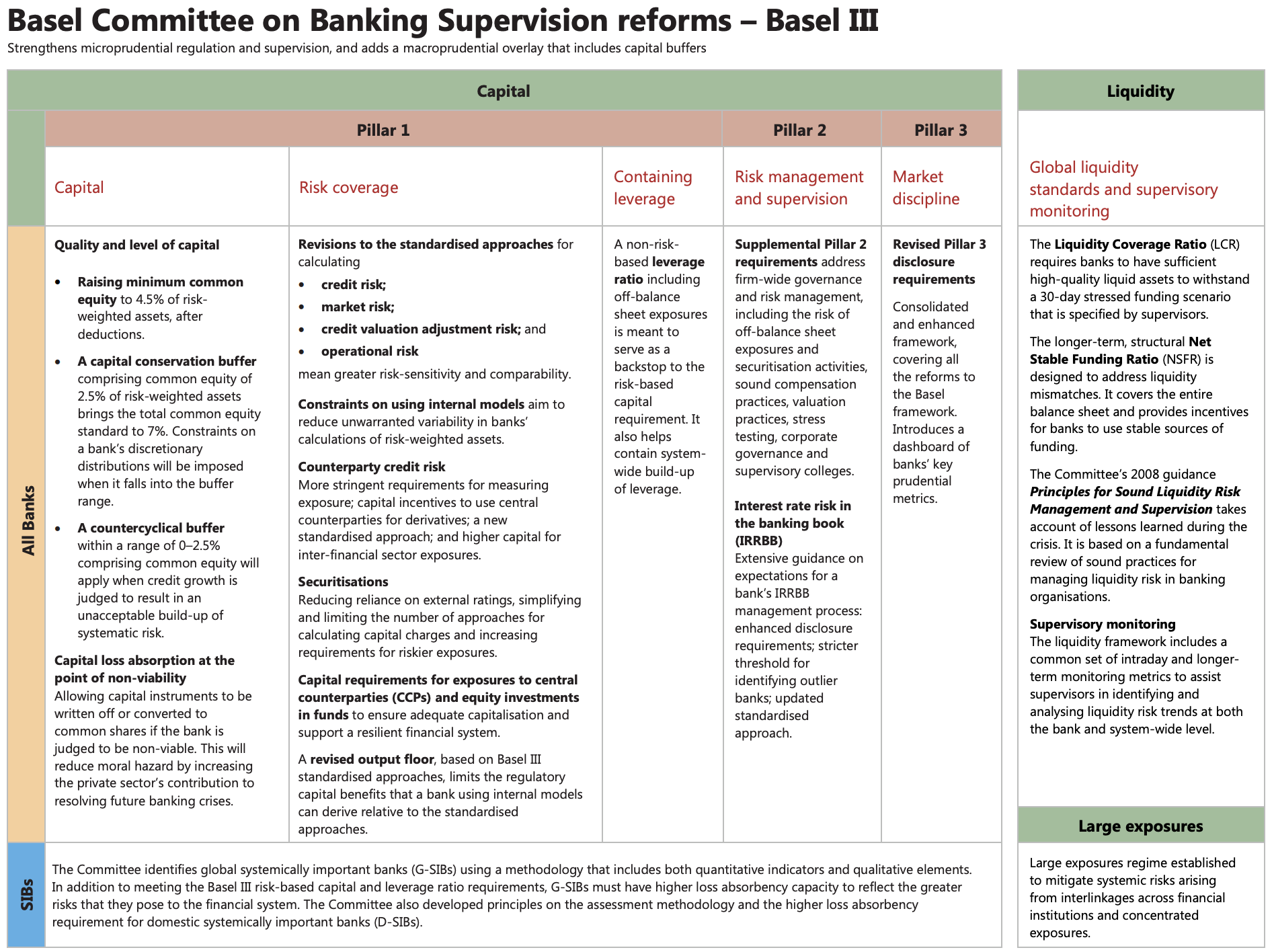
An important aspect is
Afftecting all bank and SIBS (systematically international bank)
Capital
Basel 3 explanation on video
SIBS
The Committee identifies global systemically important banks (G-SIBs) using a methodology that includes both quantitative indicators and qualitative elements. In addition to meeting the Basel III risk-based capital and leverage ratio requirements, G-SIBs must have higher loss absorbency capacity to reflect the greater risks that they pose to the financial system. The Committee also developed principles on the assessment methodology and the higher loss absorbency requirement for domestic systemically important banks (D-SIBs).
Liquidity
the International globe.
out An what's independent happening organization at based the in Bank Geneva, for Switzerland, International ISO Settlements develops by voluntary following consensus our The standards latest Basel worldwide. press Framework
The releases Basel and framework announcements.
Stress test on capital video
The Commission Basel for Committee Europe
on Banking Supervision is a committee of the Bank for International Settlements, an international organization that promotes central banking and financial stability. The BCBS was established in 1930 by the Basle Accords to regulate capital adequacy requirements for banks worldwide. It has since been responsible for setting minimum standards for bank regulation around the world. CET1 capital requirements
This measure intends to restrict the build-up of leverage in the banking sector and reinforce the risk-based requirements with a simple, non-risk-based "backstop" measure. (bis.org)
Innovation and fintech Coronavirus (Covid-19) Climate change & green finance BIS authors Annual Economic Report Quarterly Review Working Group on Financial Stability Other publications Committees & associations Committees & associations The BIS hosts nine international organisations engaged in standard setting and the pursuit of financial stability through the Basel Process. (bis.org)
Criticisms The Institute of International Finance, a 450-member banking trade association located in the United States, protested the implementation of Basel III due to its potential to hurt banks and slow down economic growth. (corporatefinanceinstitute.com)
Terima kasih sudah mampir! Yuk isi survey berikut!
read moreKali ini kita akan bahas kenapa sekolah PhD itu lama! Tanpa panjang lebar, berikut cara ngeles gw! Maksudnya berikut alasannya! Hope its relate with you!
read moreHere is my documentation after learning the introduction of AI in courserERA.
read moreThe Cloud Natural Language API lets you extract entities from text, perform sentiment and syntactic analysis, and classify text into categories.
read moreNull result in economic is when the output does not supporting your hypothesis
read more
Collaboratively administrate empowered markets via plug-and-play networks. Dynamically procrastinate B2C users after installed base benefits. Dramatically visualize customer directed convergence without
Comments